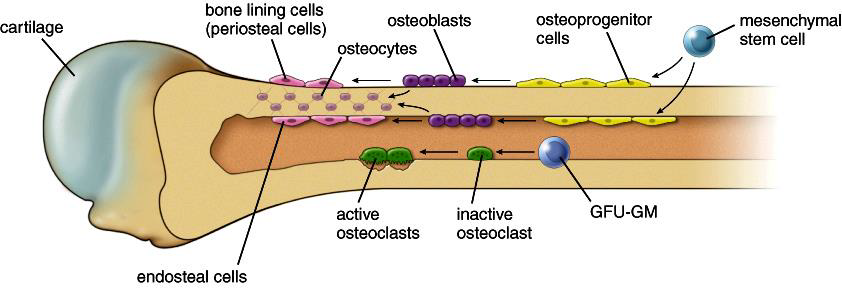
Osteogenic cells that are mitotically active stem cells found in periosteum and endosteum in growing bones are squamous cells can differentiate into osteoblasts.
Active stem cells in periosteum and endosteum.
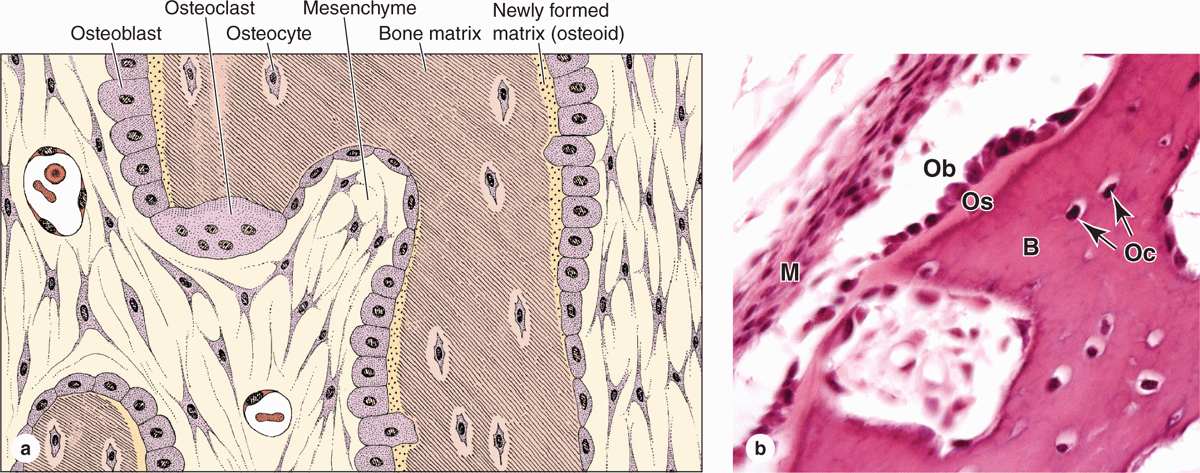
Bone forming cells that secrete unmineralized bone matrix called osteoid.
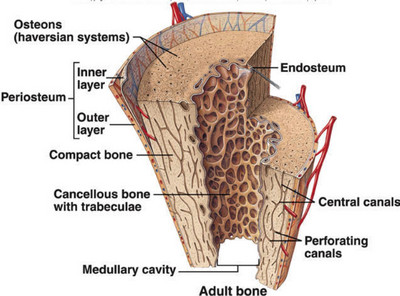
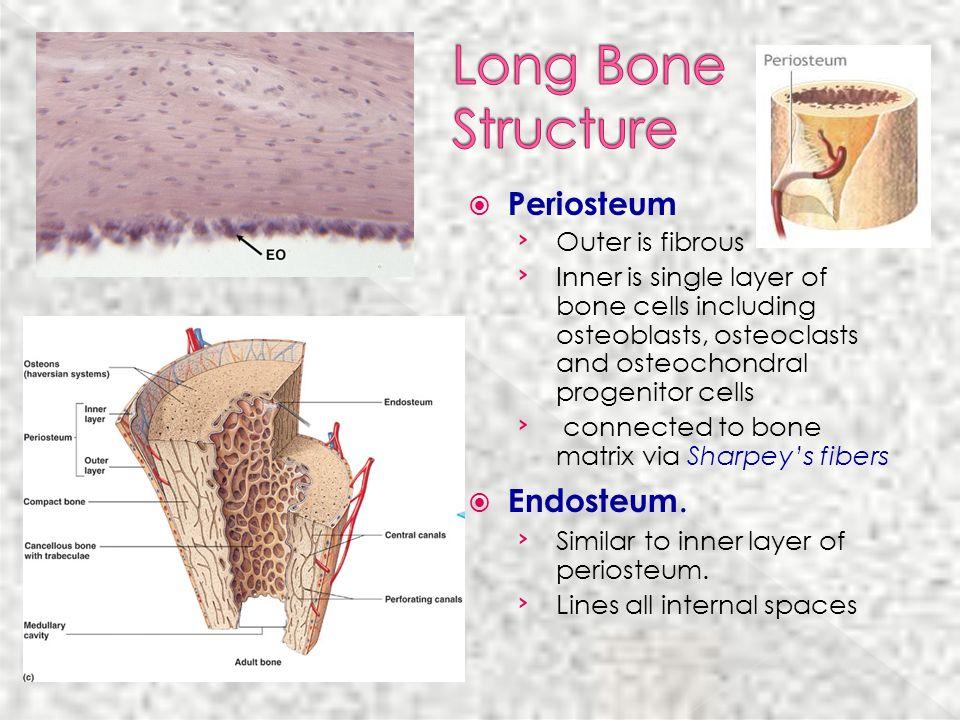
Moreover periosteum consists of two layers while endosteum is a thin layer.
Mature bone cell that occupy lacunae.
The first ones are cells that contribute to the formation of bone while the latter represent cells that actually dissolve the bone.
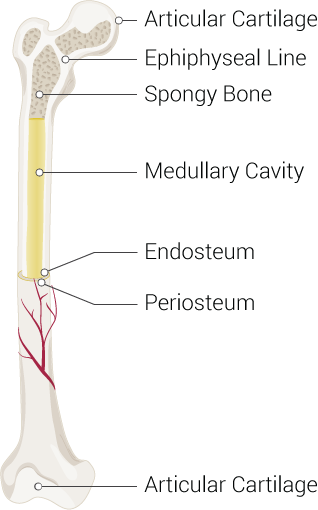
The main difference between periosteum and endosteum is that the periosteum covers the outer surface of bones whereas endosteum covers the inner surface of bones furthermore periosteum occurs in all bones except at the joints of long bones while endosteum occurs in all bones.
Mitotically active stem cells found in the membranous periosteum and endosteum.
They are flattened or squamous cells.
Located deep to periosteum and superficial to endosteum and extend around entire circumference of the diaphysis and resist twisting of long bone.
The endosteum contains osteoprogenitor cells but does not appear to contain either mscs or hematopoietic stem cells hscs.
However a portion of hscs 20 can be found near within 10 μm of the endosteum suggesting cells within the endosteum may directly.
Break down the bone.
When stimulated create osteoblasts or bone lining cells.
Secures the periosteum to bone and.
Cell that secretes the bone matrix.
Canals that lie at right angles to the long axis of the bone and connect blood and nerve supply of the periosteum to the centeral canal.
In fact both endosteum and periosteum play an active role in the healing of.
Mitotically active stem cells found in the endosteum and periosteum.
The distinct cellular contributions of periosteum endosteum and bone marrow suggested the presence of both intrinsic dissimilarities within these residing stem cell populations and differences in the tissue environment.
In bone healing periosteum and endosteum both give rise to osteoblasts whereas periosteum is the only source of chondrocytes.
Mitotically active stem cells in periosteum and endosteum when stimulated they differentiate into osteoblasts or bone lining cells some remain osteogenic stem cells.
Mitotically active stem cells in periosteum and endosteum when stimulated they differentiate into osteoblasts or bone lining cells some remain as osteogenic stem cells.
Osteoclasts can also be present in the endosteum in regions of active bone resorption.
The structural unit of compact bone.
They differentiate into osteoblasts.
Mitotically active stem cells found in the periosteum and endosteum.